The Whole Foods, Plant-Based Diet (abbreviated as WFPB) is a dietary regimen based on whole, plant-derived foods that facilitate weight loss and detoxification.
This vegan diet for weight loss also improves heart health, establishing itself as a commendable dietary (and lifestyle) choice. However, there are some contraindications that may make it unsuitable for everyone.
We’ll explain the pros and cons and what it entails.
**Eating These Foods Can Seriously Help Reduce Stress**
What You Should Know About the WFPB Diet
What Is It?
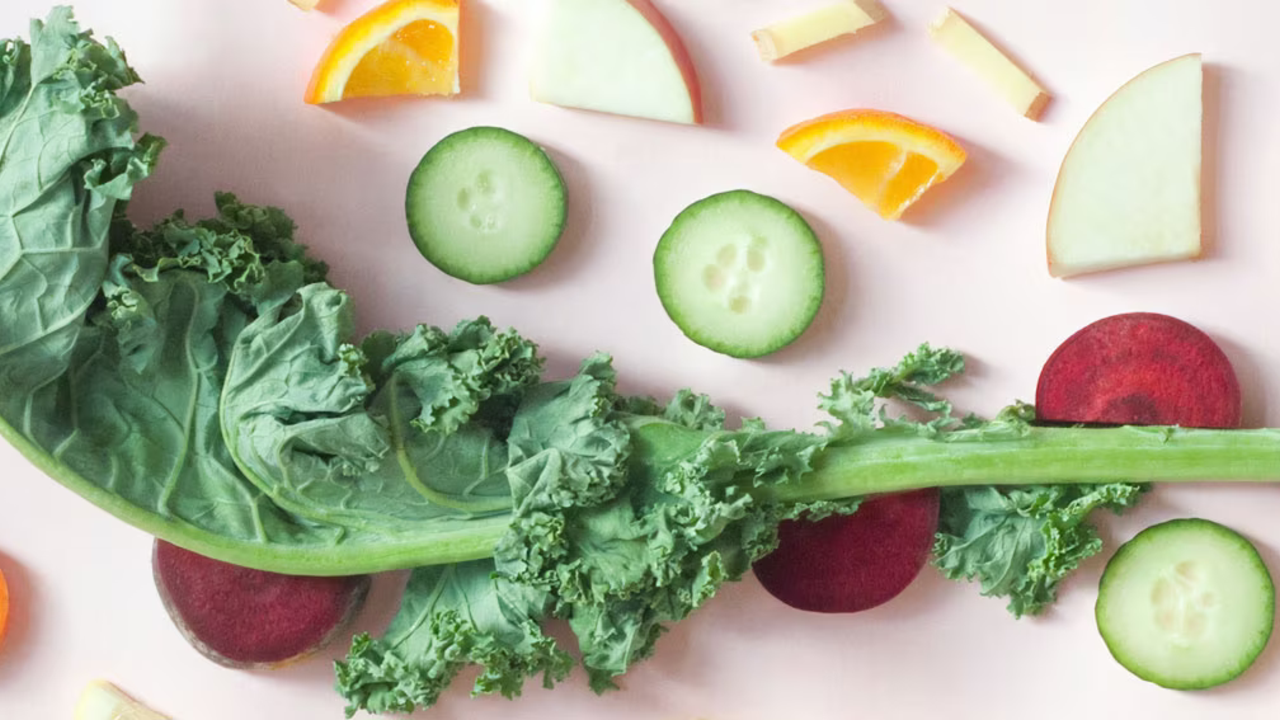
The Whole Foods, Plant-Based Diet, abbreviated as WFPB, centers around consuming whole foods, which are unprocessed and free from harmful refined sugars.
In addition to whole foods, this diet emphasizes plant-based foods while eliminating the intake of animal-derived products.
So, not only meat and fish, but also milk and eggs are to be avoided.
Breakfast on the WFPB Diet
For breakfast, you can have a glass of plant-based milk like coconut milk, soy milk, rice milk, or oat milk, according to your preference.
It’s advisable to accompany it with some nuts and a bowl of berries, for a rich source of omega-3 fats and antioxidants that will energize you and promote well-being.
If you prefer a quick breakfast, you can simply have plant-based milk and a cup of coffee, keeping a couple of nuts and a handful of berries for a mid-morning snack.
** 14 Ways To Help Ease Sugar Cravings This Fall**
Lunch Choices
For lunch, opt for a fresh salad in warm seasons or a soup in cold ones.
The key is to base your lunch around vegetables, preferably fresh, raw, and in-season.
In addition to leafy greens like lettuce, arugula, spinach, and Swiss chard, legumes such as chickpeas, lentils, and soy, as well as two allies of well-being, pumpkin seeds and avocados, are encouraged. The latter are rich in essential nutrients, from minerals to omega-3s.
Dinner Options
For dinner, focus on vegetables in a main course form.
From zucchini noodles with pesto to minestrone and chickpea velouté, emphasize the freshness of seasonal products.
Pair vegetables with pasta, spelt, rice, or quinoa, choosing the whole grain versions of grains and drizzling with extra virgin olive oil, preferably added cold at the end of cooking.
Vegan Diet for Weight Loss: What’s Allowed?
Most foods are allowed!
Apart from refined and animal-based products, almost everything is permitted. So, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds, and grains can fill your plate whenever you like, satisfying and energizing you.
Regarding fruits, aim for bananas, berries, lemons, apricots, and peaches, whether fresh, dried, or canned.
For vegetables, leafy greens, cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, carrots, potatoes, and bell peppers are preferable.
As for grains, whole-grain rice, millet, oats, quinoa, pasta, and whole-grain bread are all good choices.
Never omit legumes, favoring chickpeas, lentils, black beans, peas, and soy, including tofu and tempeh.
Highly recommend nuts and dried fruits such as cashews, peanuts, macadamia nuts, pumpkin seeds, and flax seeds, along with tahini and peanut butter variations.
As an alternative to cow’s milk and its derivatives, there are various types of plant-based milk available, from almond milk to coconut milk and soy milk; choose the one you prefer.
Several condiments are also allowed, such as soy sauce, mustard, olive oil, vinegar, spices, and herbs.
Off-Limits Foods on the WFPB Diet
You should avoid any food that undergoes refinement and industrial processing, especially those made with white flour instead of whole grain flour.
Eliminate refined sugar and bid farewell to industrially-produced sweets!
As mentioned earlier, animal-derived foods such as meat, fish, cow’s milk, and eggs are not allowed.
Pros of the Vegan Diet for Weight Loss
The WFPB diet offers several positive effects.
Apart from weight loss due to a substantial intake of fiber (which quickly satiates and reduces calorie consumption), this diet is ideal for heart health.
Whole foods and plant-based foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and legumes help counteract coronary diseases.
Plant-based foods are also rich in antioxidants that prevent cognitive and brain decline, helping the brain stay young.
This diet includes many sources of healthy fats like avocado, extra virgin olive oil, and coconut oil, providing omega-3s.
Last but not least, this type of diet is cruelty-free because it does not rely on products that involve the killing, mistreatment, and exploitation of animals.
Cons of the Vegan Diet
Meat, fish, dairy, and eggs contain essential nutrients and substances for daily needs. Eliminating them for an extended period puts you at risk of a deficiency of vital nutrients for health.
One way to avoid significant deficiencies is to take supplements or focus on certain types of foods that are an excellent source of a specific substance.
For example, for calcium, load up on green leafy vegetables, citrus, and soy milk fortified with additional calcium.
You can find iron in oats, spinach, lentils, chickpeas, and dried figs, which are also rich in zinc.
Never skip almonds for zinc; consume them daily for optimal well-being.
Iodized salt and seaweed contain iodine, while flax seeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts offer omega-3s.
To increase vitamin D levels, you can expose yourself to the sun or consume mushrooms grown with UV rays. As for vitamin B12, consume fortified foods.
There’s no risk if it’s a diet to follow for 2 to 4 weeks, but if you’re considering a long-term vegan diet, it’s advisable to consult with a doctor who can provide guidance.
**What to Eat for Breakfast to Feel Better Inside and Out**
This article first appeared on grazia.it — Author: Camilla Sernagiotto