Ensuring an adequate intake of carnitine helps maintain good health and offers additional benefits.
When talking about carnitine, supplements often come to mind, especially for those who engage in physical activity at the gym.
Elevate Your Exercise: How to Develop a Mindset for Workouts
However, carnitine can be obtained through diet. Some foods are excellent dietary sources of this nutrient, and its benefits extend beyond athletic performance.
Various studies have shown that carnitine is essential for the proper functioning of the body. It also protects against depression and aging. Therefore, ensuring its presence in your diet can have numerous health advantages.
So, what is carnitine, and which foods contain it?
What Is Carnitine
Carnitine is a nutrient that primarily helps the body produce energy and burn fatty acids, playing a crucial role in metabolism. Deficiency in this nutrient can occur for various reasons, including endocrine disorders, diabetes, and aging.
Algae: The Superfood of the Moment
Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Nutritionist’s Top 5 Menu Additions
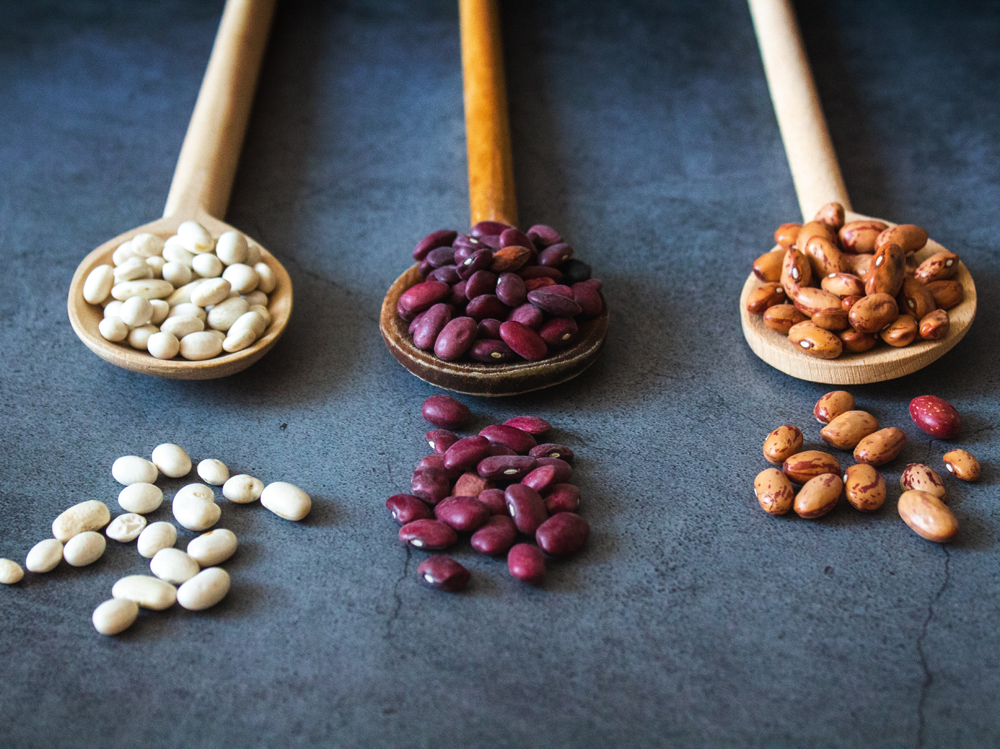

In Which Foods Can You Find It?
The main dietary sources of carnitine are red meat, poultry, and dairy products. The body can also synthesize this molecule, particularly in the liver and kidneys, from two other amino acids that must be obtained through diet: lysine and methionine. Both of these amino acids are found in significant amounts in all animal protein sources, such as meat, milk and its derivatives, and fish.
Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas, split peas, fava beans) contain lysine but lack methionine, which is present in cereals (oats, rye, barley, quinoa, buckwheat, millet, rice) and nuts (walnuts, hazelnuts, almonds, peanuts). To ensure both of these essential amino acids and help the body produce carnitine, these foods can be combined.
Photo Credits: Unsplash
This article first appeared on Grazia.it – Author: Angela Altomare