Vitamin D is closely linked to outdoor life because its production is stimulated at the skin level by exposure to sunlight.
So during winter, when days are shorter and generally less time is spent outdoors, it’s good to supplement it through diet.
Here’s why it’s important and what foods to eat to do so.
What is Vitamin D for and What Foods are Rich in it

What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is also known as the “sunshine vitamin” because its production is stimulated by exposure to sunlight and is essential for health and well-being.
It promotes the absorption of calcium at the intestinal and renal levels, an essential mineral for the health of bones and teeth.
It regulates cell growth, helps regulate muscle function, enables the proper functioning of the nervous system, and maintains brain function and good mood.
Overall, it supports the functioning of the immune system.
The Color Diet: How Does it Work?
When There is a Deficiency
The level of vitamin D drops, especially if exposure to natural light is deficient.
If most of the day is spent indoors, from home to the office, mainly using artificial light, its production will suffer.
Sunscreen creams that protect from ultraviolet rays also reduce the production of vitamin D, as does environmental pollution, dietary deficiencies, advanced age, obesity, and diseases that cause reduced intestinal absorption.

What Happens When There is Little Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency has significant consequences that can also be very serious.
From rickets in childhood, which involves bone deformities, to weaker teeth more prone to cavities.
And also psychologically: low levels of vitamin D are often associated with episodes of depression because this substance stimulates the production of serotonin, the hormone of good mood.
If it’s not possible to expose oneself to the sun, it’s important to try to supplement it through diet.
The foods richest in it are certain types of fish such as herring, sardines, and salmon, cod liver oil, tuna, oysters, mushrooms, and eggs.
However, even with a diet that includes these foods, it’s possible that the level of vitamin D may not be sufficient, so the advice is still to get some sun, even just an hour a day.
Where to Find Vitamin D in Foods
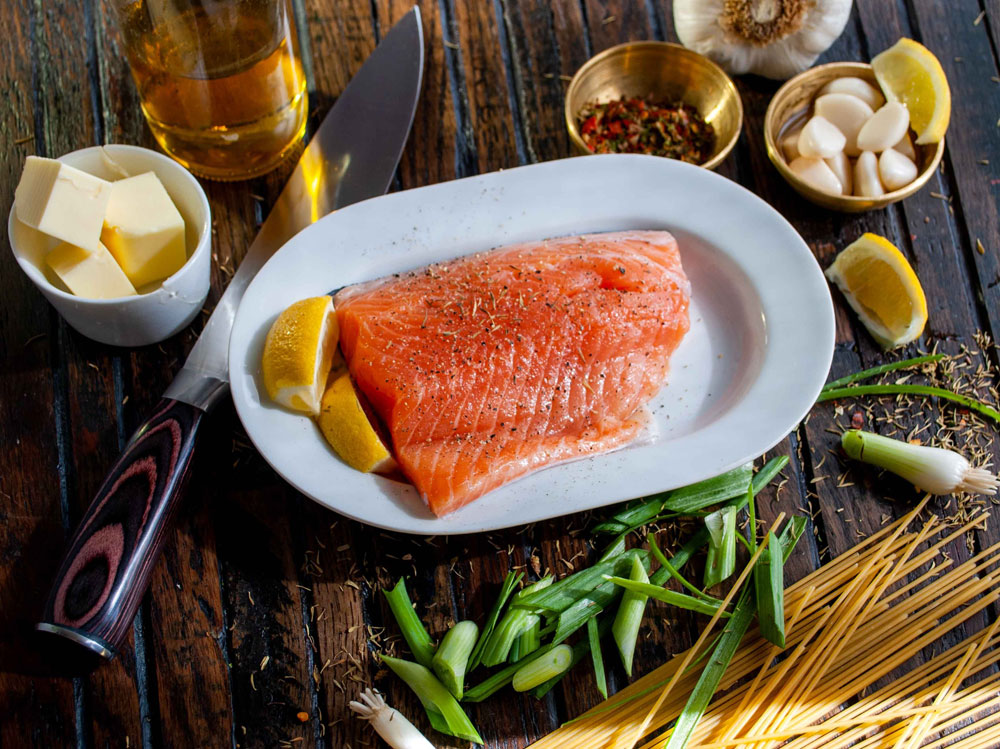

Salmon
Salmon is an excellent source of the sunshine vitamin.
100 grams of salmon contain on average between 250 and 988 IU of vitamin D.
Wild salmon contains about 988 IU of vitamin D per 100 g while farmed salmon contains an average of 250 IU.
Herring
Herring is a fish very rich in vitamin D.
Fresh, it provides 1,628 IU per serving of 100 grams, which is four times the daily requirement.
Pickled herring is also a good source, providing 680 IU per 100 grams, however, pickled foods inevitably also contain a high amount of sodium, which is detrimental to health if consumed in excess.
Other suitable types of fatty fish are halibut, mackerel, and sardines (also from the herring family).
Cod Liver Oil
Cod liver oil is a supplement that allows you to absorb nutrients that are difficult to obtain from sources other than fish.
In a teaspoon of cod liver oil, there are 450 IU of vitamin D.
It also contains many omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin A, making it a true elixir of well-being.
Canned Tuna
Canned tuna contains up to 236 IU in a serving of 100 grams, which is more than half of the daily requirement. It’s also a good source of niacin and vitamin K.
However, it would be advisable to consume a maximum of 180 g per week to avoid accumulating methylmercury, a toxin present in many types of fish that can cause serious problems to the body.
Oysters
Oysters are the mollusk richest in it.
A serving of 100 grams of oysters contains few calories (68) and 320 IU of vitamin D. And not only that: also vitamin B12, copper, and zinc, more present in oysters than in multivitamins.
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans with low-fat content and a good amount of vitamin D.
They contain about 152 IU per serving. In addition to vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids are not lacking.
They also contain about 152 mg of cholesterol per serving, which is not little. However, this is dietary cholesterol that does not have particular effects on blood cholesterol levels.
Egg Yolks
Eggs are a rich and very nutritious food.
The egg white contains most of the protein, while the yolk contains the majority of fats, vitamins, and minerals.
A yolk of eggs from chickens raised on the ground and fed with feed enriched with vitamin D has very high levels of this vitamin, up to 6,000 IU in a single yolk.
Mushrooms
The only plant source of vitamin D is mushrooms. These are able to synthesize the vitamin thanks to exposure to sunlight, just like humans.
However, it’s important to remember that mushrooms produce vitamin D2 unlike animals that produce vitamin D3, which is much more effective.
Some varieties of wild mushrooms contain up to 2,300 IU per 100 grams.
Cultivated mushrooms often have little vitamin D because they are grown in the dark. However, some growers use UV light irradiation to enhance vitamin D levels, resulting in mushrooms containing from 130 to 450 IU of vitamin D2 per 100 grams.
Why Vitamin K Matters, Especially for Women
This article first appeared on Grazia.it – Author: Camilla Sernagiotto