In recent years, carbohydrates have been unfairly attributed a bad reputation. However, they are essential for the functioning of the body and well-being, since they provide the fuel with which the body can stay in motion.
This is why it is essential for a healthy diet that they are present in every meal.
However, this does not mean that you must necessarily always eat bread, pasta, or rice, because, in fact, for the well-being of the body, it is better to vary our sources of carbohydrates as well as those of proteins, fats, and nutrients.
So, here are 12 highly healthy carbohydrate-rich foods to compose your meals.
Carbs at Night: Your Secret to Health and Happiness
Physiotherapist’s Top Pick for Natural Fat-Burning Superfood
12 Alternatives to Bread and Pasta as a Source of Carbohydrates (and Well-being)
1. Quinoa
Quinoa is an ancient cultivated plant native to the Andes, appreciated for its nutritional richness and versatility in the kitchen.
Rich in complex carbohydrates, which provide long-term energy without glycemic spikes, it is also an excellent source of protein, fiber, B vitamins, magnesium, iron, potassium, and antioxidants.
Thanks to its nutritional profile, it promotes a sense of satiety, regulates blood sugar, and supports cardiovascular and digestive health.
5 Nutrients for Healthy Hair Growth, According to a Naturopath
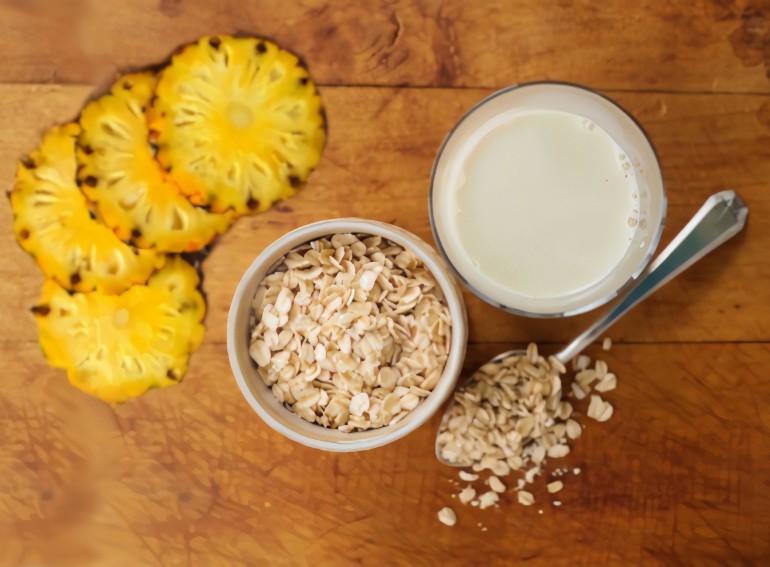

2. Oats
Oats are a popular cereal rich in complex carbohydrates. It is an excellent source of soluble fiber, which promotes intestinal regularity, reduces LDL cholesterol, and helps control blood sugar.
It also contains a range of nutrients including B vitamins, magnesium, iron, and zinc. The antioxidants present in oats, such as avenanthramides, offer benefits for cardiovascular health.
Consumed regularly, oats can help maintain body weight under control, promote a feeling of fullness, and improve metabolic health.
What to Eat for Breakfast to Feel Better Inside and Out
3. Buckwheat
Despite its name, buckwheat is actually a seed, not a cereal. It is a good source of plant protein, essential fatty acids, B vitamins, magnesium, iron, and antioxidants such as flavonoids.
Buckwheat is known to promote cardiovascular health due to its rutin content, which can improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of heart disease.
This versatile food can be consumed in various ways, as a cereal, cooking flour, or even as a base for making pasta or gnocchi.
4. Bananas
Bananas are a healthy and nutritious fruit, rich in both simple and complex carbohydrates, such as glucose, fructose, and starch. They are also a good source of fiber, potassium, B vitamins, vitamin C, and antioxidants such as dopamine and catechin.
Thanks to their low glycemic index but high fiber content, bananas can help regulate blood sugar and promote satiety.
Additionally, the potassium present in them supports muscle and nerve function, heart health, and blood pressure control.
Going Bananas for the Tropical Fruit: Some Health Benefits & Risks
5. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are one of the richest vegetables in complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are an excellent source of vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants such as carotenoids and anthocyanins.
The slow-release carbohydrates in sweet potatoes provide sustained energy without glycemic spikes.
Moreover, sweet potatoes contain beta-carotene, which may play a role in preventing cardiovascular diseases and promoting eye health. Their high potassium content supports heart health and blood pressure control.
6. Beets
Beets are edible roots rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are particularly known for their high folate, vitamin C, potassium, and manganese content.
Additionally, they are rich in antioxidants such as betalains, which can help reduce inflammation and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
The nutritional profile of beets benefits digestive and heart health, as their nitrate content may help reduce blood pressure and improve blood circulation.
Healthy (and Vegan) Snacks: 4 Recipes
7. Oranges
This juicy citrus fruit is rich in simple carbohydrates, mainly in the form of natural sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose. It is also an excellent source of vitamin C, B vitamins, potassium, and dietary fiber.
The dietary fiber in oranges promotes satiety, regulates blood sugar, and supports digestive health, while their vitamin content supports the immune system, reduces inflammation, and protects cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Finally, regularly consuming oranges can contribute to heart health, as their potassium content can help reduce blood pressure and improve vascular function.
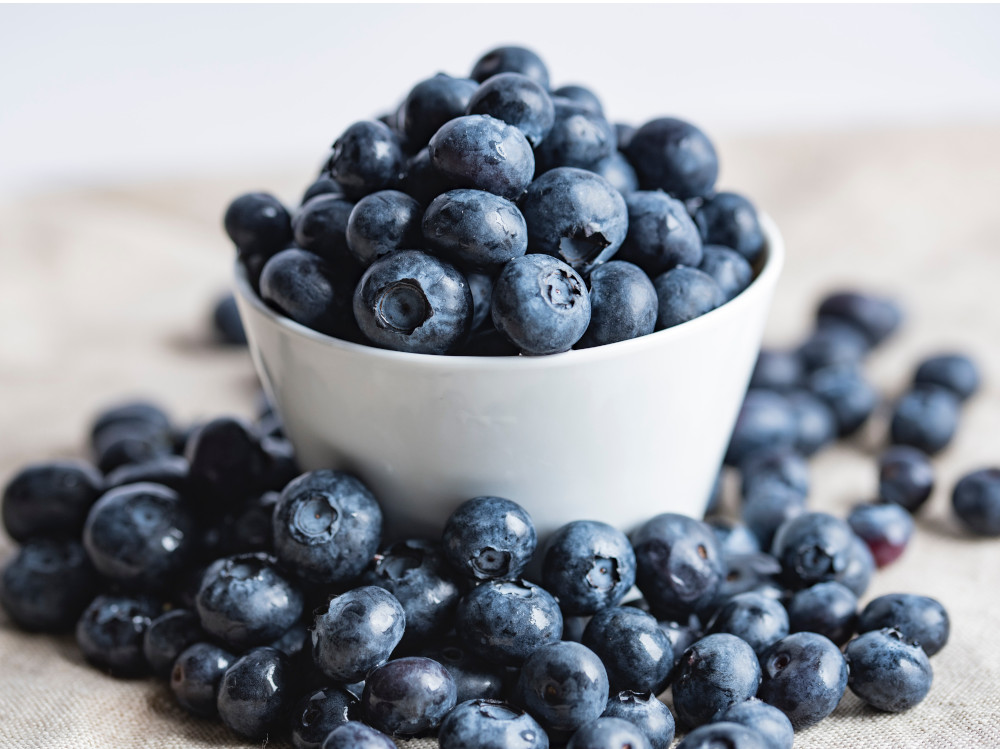

8. Blueberries
Blueberries are rich in complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. They are particularly known for their high anthocyanin content, a type of flavonoid that gives them their characteristic blue-violet color and offers numerous health benefits.
Blueberries are also a good source of B vitamins, vitamin C, potassium, and dietary fiber; and thanks to their high antioxidant content, blueberries can help reduce inflammation, protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, and improve memory and cognitive functions.
Finally, the fiber in blueberries promotes intestinal regularity, reduces the risk of heart disease, and supports weight control.
9. Grapes
Each grape is rich in simple carbohydrates such as glucose and fructose, but also in complex carbohydrates such as starch. This fruit is a good source of B vitamins, vitamin C, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and dietary fiber.
Thanks to their polyphenol content, such as resveratrol, grapes offer numerous health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cardioprotective properties. Consuming them can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, improve cognitive function, and protect skin health.
Do Grapes Make You Gain Weight?
10. Apples
Rich in complex carbohydrates, mainly in the form of dietary fiber and natural sugars such as glucose and fructose, apples are also a good source of B vitamins, vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants such as polyphenols.
Thanks to their high fiber content, they promote satiety, regulate blood sugar, and support digestive health. Additionally, the antioxidants present in apples can help reduce inflammation, protect cells from damage caused by free radicals, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
11. Chickpeas
Chickpeas are versatile legumes rich in carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Additionally, chickpeas are rich in plant protein and dietary fiber, which promote satiety, regulate blood sugar, and support digestive health.
This legume also has a high content of B vitamins, iron, zinc, magnesium, and potassium.
Thanks to its nutritional profile, chickpeas can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Their regular consumption can also be beneficial for intestinal health, as their dietary fiber promotes the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria.
How Many Times per Week Should You Eat Legumes?
12. Red beans
Red beans are nutritious legumes rich in slow-release carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They also contain plant proteins, fiber, B vitamins, iron, zinc, potassium, and antioxidants such as flavonoids.
Thanks to their nutritional profile, red beans can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
This article first appeared on Grazia.it