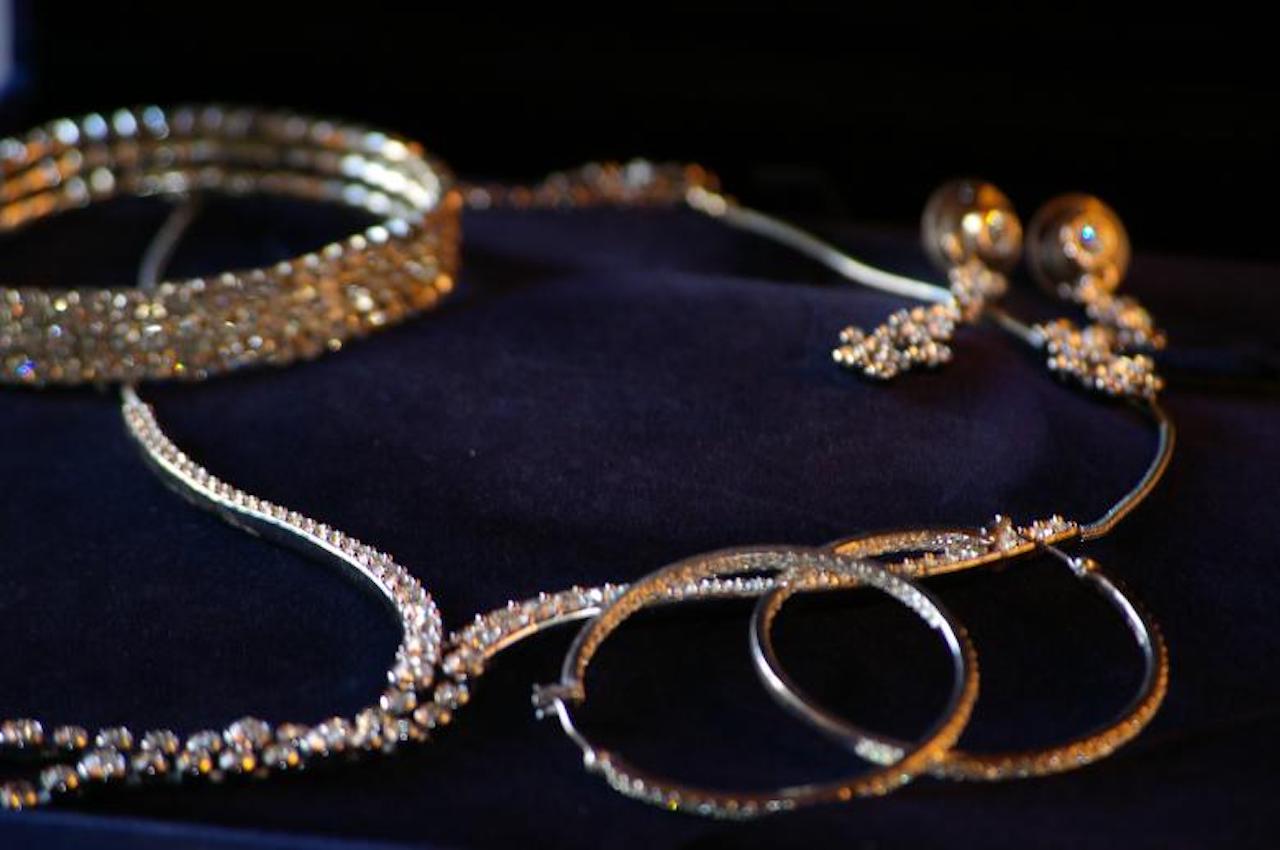
Lab diamonds have been around for a while. The first commercially practical synthetic diamond was created by General Electric (GE) on December 16, 1954. These stones made their big breakthrough the same year, though they have been known to humanity since the 1940s.
Unlike today, lab-grown diamonds were not always known to the public. This significantly undermined their similarity to mined diamonds in hardness and high conductivity.
But come the 1970s, diamond laboratories finally started taking an interest in lab diamonds due to their resemblance to their natural counterparts. With time and as the interest grew, lab processes improved considerably; the end product could compete with naturally mined diamonds in terms of their 4Cs (cut, clarity, color, and carat).
Due to its accessibility and brilliance, the sparkling gemstone immediately became well-known. Its flawless composition also helped it gain traction faster.
Mined diamonds develop in natural environments, making them full of imperfections, such as dirt and mud. The creation of synthetic diamonds happens under the supervision of scientists, who guarantee that they are perfect, pure, and free of any impurities.
The Upsurge of Lab Diamonds
Over the past 30 years, lab-grown diamonds have acquired a significant role in industrial applications. The effect has been so phenomenal that mined diamonds currently make up less than 1% of the world’s supply of industrial diamonds.
This leads to the speculation that the recent developments in lab diamond production and their expanding high-tech applications may result in the displacement of mined gem-quality diamonds in the near future.
What Makes Lab Diamonds Worth the Hype
Buyers are drawn to lab-made diamonds because of their price, transparency, and environmental considerations, as reported by the Antwerp World Diamond Centre (AWDC).
As a result, this market segment is rising by 15% to 20% yearly. The growth is anticipated to continue as more jewelers begin offering lab-created diamonds and more laboratories open.
But one would be tempted to ask why.
The ability to generate higher-quality diamonds faster and cheaper has increased drastically over the years. The process is further intensified by substantial advancements in lab-diamond technology, which has also caused competition between companies producing mined and lab diamonds. The race for a higher market share also affects prices, much to consumers’ delight.
Per a report, a lab-grown diamond now costs $300 to $500 per carat instead of $4,000 per carat in 2008 because its creation now touches fewer hands, thanks to technical advancements. This enables people to get more value for their money without compromising quality or size.
Besides, since they are evaluated using the same method as natural diamonds, the choice has become cheaper yet better and more environmentally friendly.
Transforming Choices
Many still connect the terrible environmental and labor issues surrounding conflict or “blood” diamonds with diamond mining. These stones were dug out of the ground by hand in unregulated mines that frequently employed vulnerable employees, including young children.
Illegal diamond trade between 1989 and 2003 financed several civil wars in the west and central Africa. This prompted the creation of the Kimberley Process – an international trade certification started in 2003 to prevent the widespread sale of conflict diamonds. The program would later catalyze the diamond industry’s ongoing efforts at restoration.
Along with concerns about how the mining industry treats its workforce and communities ethically, it has also come under fire for its carbon imprint. Thus, most millennials have changed their shopping habits to promote products that don’t harm the environment.
This man-made diamond jewelry will constitute an ethical purchase because it doesn’t involve mining during manufacturing and is made possible through HPHT (high-pressure, high temperature) and CVD (chemical vapor deposition) techniques.
On the other hand, mining pollutes the air and water, ruins natural landscapes, and endangers flora and animals.
Another utility of lab-grown diamonds is that you can trace their origins and feel confident in your purchase. Where it may be demanding to track a mined stone’s position and formation date, lab diamonds allow you to find out where they come from.
Buying lab-grown diamonds is always a wise decision; various reasons and evidence support the claim that they offer the most long-lasting and sustainable options. Moreover, they are an investment that every jeweler enthusiast should make, given their affordability and aptitude to be devoid of guilt and unethical practices.